Workflow Variables
Understanding how information flows through your workflow is key to building powerful automations. Variables are the data that moves between steps, building up knowledge as your workflow executes.
Start Variables
The Start node is where you define what information your workflow needs to run. These start variables are the initial variables that kick off your entire workflow - think of them as the ingredients your workflow needs to do its job. You can add or modify these inputs at any time while building your workflow - nothing is set in stone.
Start Variable Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| String | Any type of text (names, descriptions, messages) |
| Number | Numeric values (quantities, scores, prices) |
| Boolean | True/false or Yes/no choices |
| Array | Lists of items (multiple email addresses, product names) |
| Object | Structured data (complete customer record) |
| File | Document uploads (PDF, spreadsheets, images) |
Each Start variable can be configured with a:
| Default value | A pre-filled suggestion that users can override |
| Help text | Instructions that explain what information is needed |
| Required status | Mark whether this input must be provided or is optional |
Example
Let's say you're building a customer feedback workflow. You might create:
- A required "customer_email" text input with help text: "Enter the customer's email address"
- An optional "previous_interactions" list input for context
- A required "feedback_type" choice between "complaint," "suggestion," or "praise"
Variable Store
As your workflow runs, it builds up a context - think of it like a shared memory bank that grows with each step. This context starts small (just your start variables) and grows richer as each node adds its result. By the end of your workflow, you have a complete record of everything that was gathered, calculated, or decided along the way.
Why this matters: Later steps in your workflow can make smarter decisions because they have access to all the accumulated knowledge from earlier steps. For example, a final email step can reference the customer's name from step 1, their purchase history from step 3, and the discount calculation from step 5 - all from the shared context.
Using Variables in Workflow Nodes
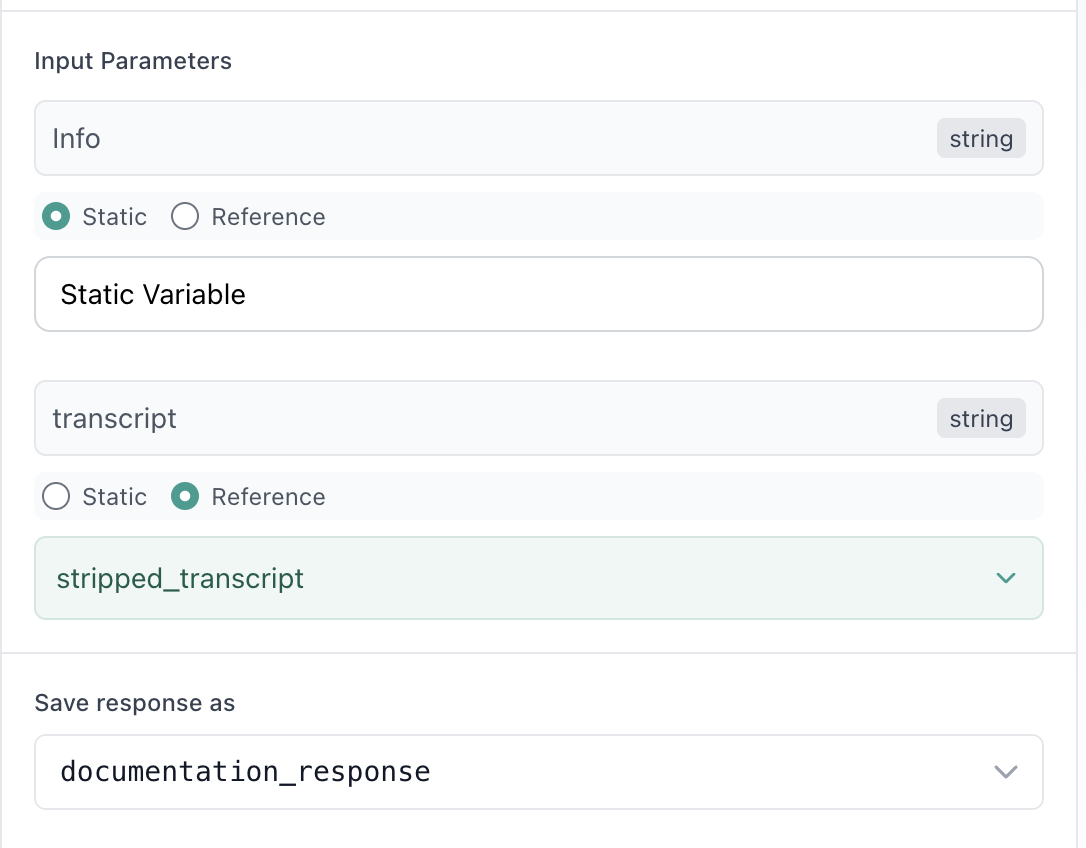
Each node in your workflow accepts input variables to do its work. These might be variables to an integration for an API call, or pre-defined blocks within a prompt such as a block of text to be classified. Input variables can be passed to a node in two ways:
Static Values - Fixed values that never change:
- Set a specific value that remains constant every time the workflow runs
- Useful for configuration settings, standard messages, or fixed thresholds
- Example: Always use "[email protected]" as the reply-to addres
Reference Values - Dynamic values from other variables:
- Pull in values from the Start node inputs or any previous node's output
- The value changes based on what's in your workflow's context
- Example: Use the
customer_emailfrom the Start node orsentiment_scorefrom a previous analysis
Output Variables
Every node produces an output variable containing its result. This vairable can be renamed - and is made available to all subsequent nodes